Robots need to be adaptable, readily learning new skills and adjusting to their surroundings. Yet traditional training methods can limit a robot’s ability to apply learned skills in new situations. This is often due to the gap between perception and action, as well as the challenges in transferring skills across different contexts.
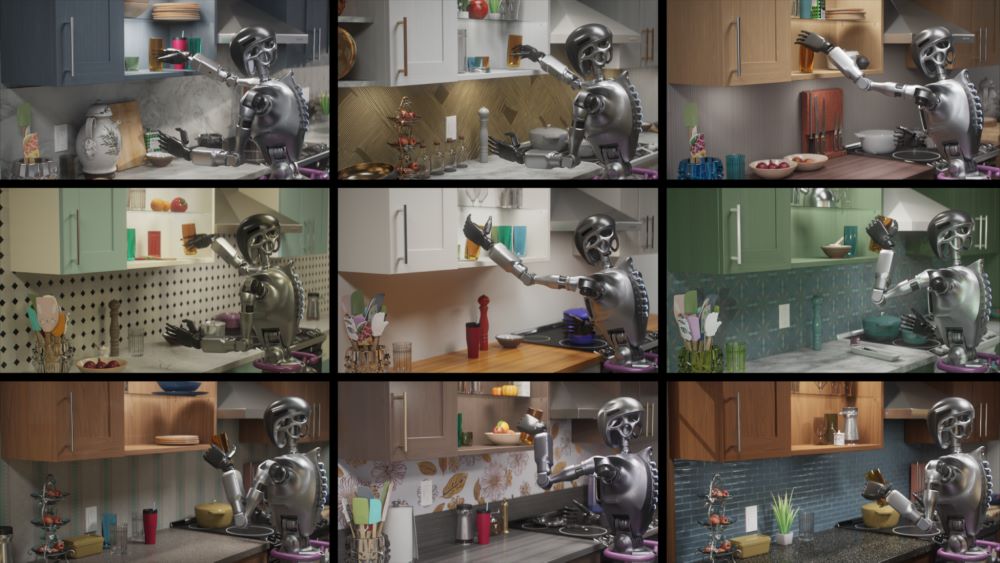

NVIDIA Isaac Lab is an open-source modular framework for robot learning that addresses these limitations. The Isaac Lab modular high-fidelity simulations for diverse training environments provide physical AI capabilities and GPU-powered physics simulations.
Isaac Lab supports both imitation learning (mimicking humans) and reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error), providing flexibility in training approaches for any robot embodiment. It offers a user-friendly environment for training scenarios that helps robot makers add or update robot skills with changing business needs.
Many industry collaborators are using Isaac Lab to train humanoid robots efficiently. These include Fourier Intelligence, whose GR1 humanoid robot has human-like degrees of freedom, and Mentee Robotics, whose MenteeBot is built for household-to-warehouse applications.

ORBIT-Surgical is a simulation framework based on Isaac Lab that trains robots like the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) to assist surgeons and reduce their mental workload. The framework uses reinforcement learning and imitation learning, running on NVIDIA RTX GPUs, to enable robots to manipulate both rigid and soft objects. Additionally, NVIDIA Omniverse helps generate high-fidelity synthetic data that can be used to train AI models for segmenting surgical tools in real-world hospital operating room videos.
Boston Dynamics is using Isaac Lab and NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin to enable simulated policies to be directly deployed for inference, simplifying the deployment process. For more information, see Closing the Sim-to-Real Gap: Training Spot Quadruped Locomotion with NVIDIA Isaac Lab.
This post provides an overview of key NVIDIA Isaac Lab features and a preview of the Isaac Lab ecosystem collaborators in the NVIDIA Humanoid Robot Developer Program. It also explains how to scale robot workflows using the NVIDIA OSMO platform.
Isaac Lab features for accelerated robot learning
Key features available in Isaac Lab include reinforcement and imitation learning for seamless and effective robot policy training, fast and accurate physics simulation provided by PhysX, tiled rendering APIs for vectorized rendering, domain randomization for improving robustness and adaptability, and support for running in the cloud.
Multiple robot training techniques in one tool: Isaac Lab is a simulation application that enables robot learning through reinforcement learning and imitation learning.

Reinforcement learning (RL): Robots learn through trial and error, making them more adaptable to new situations and potentially exceeding human performance for some tasks. However, RL can be slow and requires carefully designed reward functions to guide the robot’s learning. Isaac Lab provides support for RL through wrappers to different libraries, which convert environment data into function argument and return types.
With Isaac Lab 1.2, we’ve released an LLM-to-Reward Function reference example for reinforcement learning.
Imitation learning
Robots learn by mimicking human demonstrations. This method is ideal for tasks with specific movements or behaviors, requiring less data and leveraging human expertise. Support for imitation learning comes through the learning framework Robomimic and enables saving data in HDF5.
Flexibility with task design workflows
Build robot training environments in two ways, manager-based or direct. With the manager-based workflow, you can easily switch out different parts of the environment. To optimize performance for complex logic, the direct workflow is recommended.
Tiled rendering (RGB, Depth, and Semantics)
Isaac Lab is currently the only industry tool offering high-fidelity rendering for robot learning, helping reduce the sim-to-real gap. Tiled rendering reduces rendering time by consolidating input from multiple cameras into a single large image. It provides a streamlined API for handling vision data, where the rendered output directly serves as observational data for simulation learning.

Vectorized APIs
Tap into enhanced View APIs for improved usability, eliminating the need to pre-initialize buffers, and caching indices for different objects in the scene, in addition to support for multiple view objects in the scene.
Easy deployment to public clouds
Supports deployment on AWS, GCP, Azure, and Alibaba Cloud, with Docker integration for efficient RL task execution in containers, as well as seamless scaling of multi-GPU and multi-node jobs using OSMO.
Accurate physics simulation
Tap into the latest GPU accelerated PhysX version through Isaac Lab, including support for deformables, ensuring quick and accurate physics simulations augmented by domain randomizations.
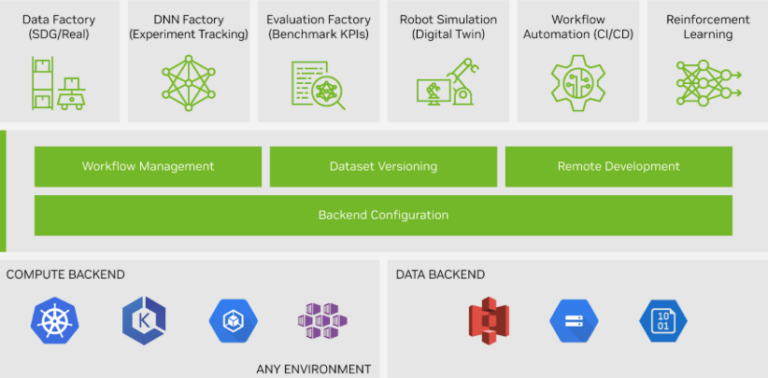
Scale robot workflows with NVIDIA OSMO
NVIDIA OSMO is a cloud-native workflow orchestration platform that helps to orchestrate, visualize, and manage a range of tasks. These include generating synthetic data, training foundation models, and implementing software-in-the-loop systems for any robot embodiment.
With NVIDIA OSMO, enterprises can train robots efficiently without extensive in-house IT expertise. Request early access to NVIDIA OSMO.